Are Fallen Arches Flat Feet?
Overview

Left untreated, fallen arches, or flat feet, not only cause pain but can lead to other serious foot and joint problems such as shin splints. With proper shoe selection and exercises you can begin to strengthen and restore the arches in your feet. If you are concerned about your fallen arches, consult with an experienced podiatrist.
Causes
Most cases of flatfeet are simply the result of normal development. When that is not the case, the condition can be caused by a number of factors, including the following, Age, disease, injury, obesity or being overweight, physical abnormality, pregnancy. Flattened arches in adults may result from the stresses of aging, weight gain, and the temporary increase in elastin (protein in connective tissue) due to pregnancy. In some cases, flatfeet are caused by a physical abnormality, such as tarsal coalition (two or more bones in the foot that have grown together) or accessory navicular (an extra bone along the side of the foot). The effects of diseases such as diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis can lead to flatfeet. An injury (e.g., bone fracture, dislocation, sprain or tear in any of the tendons and ligaments in the foot and leg) also can cause flatfeet.
Symptoms
Arches can be seen as ?rolling downward? or collapsing when walking. Pain may present in lower back, hips or knees. Pain may be present on the bottom of the heels, within the arch, within the ankles or even the forefoot. Swelling can occur. Pain may occur in the anterior leg muscles.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. A physical and foot exam will be done. Flat feet can be diagnosed by appearance. To determine if the foot is rigid, you may be asked to do some simple tasks.
how to fix fallen arches
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment of flat feet really depends on how far the damage has progressed. Conservative treatments often include immobilization (often by cast or brace) to reduce inflammation. Your doctor may also recommend anti-inflammatory medication (like ibuprofen) to get your inflamed tendon to calm down a bit. Orthotics can also offer significant relief. If these treatments fail to significantly improve symptoms, then surgery may be your best option to get the structure of your body back where it needs to be. Your podiatrist can discuss surgical options with you in great depth.
Surgical Treatment

Rarely does the physician use surgery to correct a foot that is congenitally flat, which typically does not cause pain. If the patient has a fallen arch that is painful, though, the foot and ankle physicians at Midwest Orthopaedics at Rush may perform surgery to reconstruct the tendon and "lift up" the fallen arch. This requires a combination of tendon re-routing procedures, ligament repairs, and bone cutting or fusion procedures.
After Care
Time off work depends on the type of work as well as the surgical procedures performed. . A patient will be required to be non-weight bearing in a cast or splint and use crutches for four to twelve weeks. Usually a patient can return to work in one to two weeks if they are able to work while seated. If a person's job requires standing and walking, return to work may take several weeks. Complete recovery may take six months to a full year. Complications can occur as with all surgeries, but are minimized by strictly following your surgeon's post-operative instructions. The main complications include infection, bone that is slow to heal or does not heal, progression or reoccurrence of deformity, a stiff foot, and the need for further surgery. Many of the above complications can be avoided by only putting weight on the operative foot when allowed by your surgeon.

Left untreated, fallen arches, or flat feet, not only cause pain but can lead to other serious foot and joint problems such as shin splints. With proper shoe selection and exercises you can begin to strengthen and restore the arches in your feet. If you are concerned about your fallen arches, consult with an experienced podiatrist.
Causes
Most cases of flatfeet are simply the result of normal development. When that is not the case, the condition can be caused by a number of factors, including the following, Age, disease, injury, obesity or being overweight, physical abnormality, pregnancy. Flattened arches in adults may result from the stresses of aging, weight gain, and the temporary increase in elastin (protein in connective tissue) due to pregnancy. In some cases, flatfeet are caused by a physical abnormality, such as tarsal coalition (two or more bones in the foot that have grown together) or accessory navicular (an extra bone along the side of the foot). The effects of diseases such as diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis can lead to flatfeet. An injury (e.g., bone fracture, dislocation, sprain or tear in any of the tendons and ligaments in the foot and leg) also can cause flatfeet.
Symptoms
Arches can be seen as ?rolling downward? or collapsing when walking. Pain may present in lower back, hips or knees. Pain may be present on the bottom of the heels, within the arch, within the ankles or even the forefoot. Swelling can occur. Pain may occur in the anterior leg muscles.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. A physical and foot exam will be done. Flat feet can be diagnosed by appearance. To determine if the foot is rigid, you may be asked to do some simple tasks.
how to fix fallen arches
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment of flat feet really depends on how far the damage has progressed. Conservative treatments often include immobilization (often by cast or brace) to reduce inflammation. Your doctor may also recommend anti-inflammatory medication (like ibuprofen) to get your inflamed tendon to calm down a bit. Orthotics can also offer significant relief. If these treatments fail to significantly improve symptoms, then surgery may be your best option to get the structure of your body back where it needs to be. Your podiatrist can discuss surgical options with you in great depth.
Surgical Treatment

Rarely does the physician use surgery to correct a foot that is congenitally flat, which typically does not cause pain. If the patient has a fallen arch that is painful, though, the foot and ankle physicians at Midwest Orthopaedics at Rush may perform surgery to reconstruct the tendon and "lift up" the fallen arch. This requires a combination of tendon re-routing procedures, ligament repairs, and bone cutting or fusion procedures.
After Care
Time off work depends on the type of work as well as the surgical procedures performed. . A patient will be required to be non-weight bearing in a cast or splint and use crutches for four to twelve weeks. Usually a patient can return to work in one to two weeks if they are able to work while seated. If a person's job requires standing and walking, return to work may take several weeks. Complete recovery may take six months to a full year. Complications can occur as with all surgeries, but are minimized by strictly following your surgeon's post-operative instructions. The main complications include infection, bone that is slow to heal or does not heal, progression or reoccurrence of deformity, a stiff foot, and the need for further surgery. Many of the above complications can be avoided by only putting weight on the operative foot when allowed by your surgeon.
Heel Painfulness The Root Causes, Signals And Treatment Alternatives
Overview

Heel pain is often a symptom caused by one of two conditions: Plantar Fasciitis or Achilles Tendonitis. Most commonly, heel pain experienced at the bottom of the heel is caused by plantar fasciitis. Heel pain may become so severe for some that just putting weight on their feet first thing in the morning is excruciating. Walking or running may feel completely out of the question.
Causes
Heel pain is most often the result of overuse. Rarely, it may be caused by an injury. Your heel may become tender or swollen from shoes with poor support or shock absorption, running on hard surfaces, like concrete, running too often, tightness in your calf muscle or the Achilles tendon. Sudden inward or outward turning of your heel, landing hard or awkwardly on the heel. Conditions that may cause heel pain include when the tendon that connects the back of your leg to your heel becomes swollen and painful near the bottom of the foot, swelling of the fluid-filled sac (bursa) at the back of the heel bone under the Achilles tendon (bursitis). Bone spurs in the heel. Swelling of the thick band of tissue on the bottom of your foot (plantar fasciitis). Fracture of the heel bone that is related to landing very hard on your heel from a fall (calcaneus fracture).
Symptoms
Usually when a patient comes in they?ll explain that they have severe pain in the heel. It?s usually worse during the first step in the morning when they get out of bed. Many people say if they walk for a period of time, it gets a little bit better. But if they sit down and get back up, the pain will come back and it?s one of those intermittent come and go types of pain. Heel pain patients will say it feels like a toothache in the heel area or even into the arch area. A lot of times it will get better with rest and then it will just come right back. So it?s one of those nuisance type things that just never goes away. The following are common signs of heel pain and plantar fasciitis. Pain that is worse first thing in the morning. Pain that develops after heavy activity or exercise. Pain that occurs when standing up after sitting for a long period of time. Severe, toothache type of pain in the bottom of the heel.
Diagnosis
A biomechanical exam by your podiatrist will help reveal these abnormalities and in turn resolve the cause of plantar fasciitis. By addressing this cause, the patient can be offered a podiatric long-term solution to his problem.
Non Surgical Treatment
The following steps may help relieve your heel pain. Use crutches to take weight off your feet. Rest as much as possible for at least a week. Apply ice to the painful area. Do this at least twice a day for 10 to 15 minutes, more often in the first couple of days. Take acetaminophen or ibuprofen for pain. Wear proper-fitting shoes. Use a heel cup, felt pads in the heel area, or shoe insert. Wear night splints. Your doctor may recommend other treatments, depending on the cause of your heel pain.
Surgical Treatment
It is rare to need an operation for heel pain. It would only be offered if all simpler treatments have failed and, in particular, you are a reasonable weight for your height and the stresses on your heel cannot be improved by modifying your activities or footwear. The aim of an operation is to release part of the plantar fascia from the heel bone and reduce the tension in it. Many surgeons would also explore and free the small nerves on the inner side of your heel as these are sometimes trapped by bands of tight tissue. This sort of surgery can be done through a cut about 3cm long on the inner side of your heel. Recently there has been a lot of interest in doing the operation by keyhole surgery, but this has not yet been proven to be effective and safe. Most people who have an operation are better afterwards, but it can take months to get the benefit of the operation and the wound can take a while to heal fully. Tingling or numbness on the side of the heel may occur after operation.
heel spur surgery
Prevention

You can try to avoid the things that cause heel pain to start avoid becoming overweight, where your job allows, minimise the shock to your feet from constant pounding on hard surfaces, reduce the shocks on your heel by choosing footwear with some padding or shock-absorbing material in the heel, if you have high-arched feet or flat feet a moulded insole in your shoe may reduce the stresses on your feet, if you have an injury to your ankle or foot, make sure you exercise afterwards to get back as much movement as possible to reduce the stresses on your foot and your heel in particular, If you start to get heel pain, doing the above things may enable the natural healing process to get underway and the pain to improve.

Heel pain is often a symptom caused by one of two conditions: Plantar Fasciitis or Achilles Tendonitis. Most commonly, heel pain experienced at the bottom of the heel is caused by plantar fasciitis. Heel pain may become so severe for some that just putting weight on their feet first thing in the morning is excruciating. Walking or running may feel completely out of the question.
Causes
Heel pain is most often the result of overuse. Rarely, it may be caused by an injury. Your heel may become tender or swollen from shoes with poor support or shock absorption, running on hard surfaces, like concrete, running too often, tightness in your calf muscle or the Achilles tendon. Sudden inward or outward turning of your heel, landing hard or awkwardly on the heel. Conditions that may cause heel pain include when the tendon that connects the back of your leg to your heel becomes swollen and painful near the bottom of the foot, swelling of the fluid-filled sac (bursa) at the back of the heel bone under the Achilles tendon (bursitis). Bone spurs in the heel. Swelling of the thick band of tissue on the bottom of your foot (plantar fasciitis). Fracture of the heel bone that is related to landing very hard on your heel from a fall (calcaneus fracture).
Symptoms
Usually when a patient comes in they?ll explain that they have severe pain in the heel. It?s usually worse during the first step in the morning when they get out of bed. Many people say if they walk for a period of time, it gets a little bit better. But if they sit down and get back up, the pain will come back and it?s one of those intermittent come and go types of pain. Heel pain patients will say it feels like a toothache in the heel area or even into the arch area. A lot of times it will get better with rest and then it will just come right back. So it?s one of those nuisance type things that just never goes away. The following are common signs of heel pain and plantar fasciitis. Pain that is worse first thing in the morning. Pain that develops after heavy activity or exercise. Pain that occurs when standing up after sitting for a long period of time. Severe, toothache type of pain in the bottom of the heel.
Diagnosis
A biomechanical exam by your podiatrist will help reveal these abnormalities and in turn resolve the cause of plantar fasciitis. By addressing this cause, the patient can be offered a podiatric long-term solution to his problem.
Non Surgical Treatment
The following steps may help relieve your heel pain. Use crutches to take weight off your feet. Rest as much as possible for at least a week. Apply ice to the painful area. Do this at least twice a day for 10 to 15 minutes, more often in the first couple of days. Take acetaminophen or ibuprofen for pain. Wear proper-fitting shoes. Use a heel cup, felt pads in the heel area, or shoe insert. Wear night splints. Your doctor may recommend other treatments, depending on the cause of your heel pain.
Surgical Treatment
It is rare to need an operation for heel pain. It would only be offered if all simpler treatments have failed and, in particular, you are a reasonable weight for your height and the stresses on your heel cannot be improved by modifying your activities or footwear. The aim of an operation is to release part of the plantar fascia from the heel bone and reduce the tension in it. Many surgeons would also explore and free the small nerves on the inner side of your heel as these are sometimes trapped by bands of tight tissue. This sort of surgery can be done through a cut about 3cm long on the inner side of your heel. Recently there has been a lot of interest in doing the operation by keyhole surgery, but this has not yet been proven to be effective and safe. Most people who have an operation are better afterwards, but it can take months to get the benefit of the operation and the wound can take a while to heal fully. Tingling or numbness on the side of the heel may occur after operation.
heel spur surgery
Prevention

You can try to avoid the things that cause heel pain to start avoid becoming overweight, where your job allows, minimise the shock to your feet from constant pounding on hard surfaces, reduce the shocks on your heel by choosing footwear with some padding or shock-absorbing material in the heel, if you have high-arched feet or flat feet a moulded insole in your shoe may reduce the stresses on your feet, if you have an injury to your ankle or foot, make sure you exercise afterwards to get back as much movement as possible to reduce the stresses on your foot and your heel in particular, If you start to get heel pain, doing the above things may enable the natural healing process to get underway and the pain to improve.
Functional Leg Length Discrepancy Treatment Solution
Overview
The bone is lengthened by surgically applying an external fixation device to the leg. The external fixator, a scaffold-like frame, is connected to the bone with wires, pins, or both. A small crack is made in the bone and the frame creates tension when the patient or family member turns its dial. This is done several times each day. The lengthening process begins approximately five to 10 days after surgery. The bone may lengthen 1 millimeter per day, or approximately 1 inch per month. Lengthening may be slower in a bone that was previously injured. It may also be slower if the leg was operated on before. Bones in patients with potential blood vessel abnormalities, such as cigarette smokers, may also need to be lengthened more slowly. The external fixator is worn until the bone is strong enough to support the patient safely. This usually takes about three months for each inch. Factors such as age, health, smoking and participation in rehabilitation can affect the amount of time needed.
Causes
Sometimes the cause of LLD is unknown, yet the pattern or combination of conditions is consistent with a certain abnormality. Examples include underdevelopment of the inner or outer side of the leg (hemimelias) or (partial) inhibition of growth of one side of the body of unknown cause (hemihypertrophy). These conditions are present at birth, but the limb length difference may be too small to be detected. As the child grows, the LLD increases and becomes more noticeable. In hemimelia, one of the two bones between the knee and the ankle (tibia or fibula) is abnormally short. There also may be associated foot or knee abnormalities. Hemihypertrophy or hemiatrophy are rare conditions in which there is a difference in length of both the arm and leg on only one side of the body. There may also be a difference between the two sides of the face. Sometimes no cause can be found. This type of limb length is called idiopathic. While there is a cause, it cannot be determined using currect diagnostic methods.
Symptoms
The effects of limb length discrepancy vary from patient to patient, depending on the cause and size of the difference. Differences of 3 1/2 percent to 4 percent of the total length of the leg (about 4 cm or 1 2/3 inches in an average adult) may cause noticeable abnormalities when walking. These differences may require the patient to exert more effort to walk. There is controversy about the effect of limb length discrepancy on back pain. Some studies show that people with a limb length discrepancy have a greater incidence of low back pain and an increased susceptibility to injuries. Other studies do not support this finding.
Diagnosis
The only way to decipher between anatomical and functional leg length inequalities (you can have both) is by a physical measurement and series of biomechanical tests. It is actually a simple process and gets to the true cause of some runner?s chronic foot, knee, hip and back pain. After the muscles are tested and the legs are measured it may be necessary to get a special X-ray that measures both of your thighs (Femurs) and legs (Tibias). The X-ray is read by a medical radiologist who provides a report of the actual difference down to the micrometer leaving zero room for error. Once the difference in leg length is known, the solution becomes clear.
Non Surgical Treatment
The key to treatment of LLD in a child is to predict what the discrepancy is at maturity. If it is predicted to be less than 2 cm., no treatment is needed. Limb length discrepancies of up to 2 or 2.5 cm. can be compensated very well with a lift in the shoe. Beyond 2.5 cm., it becomes increasingly difficult to compensate with a left in the insole. Building up the shoe becomes uncosmetic and cumbersome, and some other way of compensating for the discrepancy becomes necessary. The treatment of LLD is long-term treatment, and involves the physician and patient?s family working together as a team. The family needs to weigh the various options available. If leg lengthening is decided on, the family needs to understand the commitment necessary to see it through. The treatment takes 6 months to a year for completion, and complications can happen. But when it works, the results are gratifying.

bestshoelifts
Surgical Treatment
Surgical treatments vary in complexity. Sometimes the goal of surgery is to stop the growth of the longer limb. Other times, surgeons work to lengthen the shorter limb. Orthopedic surgeons may treat children who have limb-length conditions with one or a combination of these surgical techniques. Bone resection. An operation to remove a section of bone, evening out the limbs in teens or adults who are no longer growing. Epiphyseal stapling. An operation to slow the rate of growth of the longer limb by inserting staples into the growth plate, then removing them when the desired result is achieved. Epiphysiodesis. An operation to slow the rate of growth of the longer limb by creating a permanent bony ridge near the growth plate. Limb lengthening. A procedure (also called distraction osteogenesis or the Ilizarov procedure) that involves attaching an internal or external fixator to a limb and gradually pulling apart bone segments to grow new bone between them. There are several ways your doctor can predict the final LLD, and thus the timing of the surgery. The easiest way is the so-called Australian method, popularised by Dr. Malcolm Menelaus, an Australian orthopedic surgeon. According to this method, growth in girls is estimated to stop at age 14, and in boys at age 16 years. The femur grows at the rate of 10 mm. a year, and the upper tibia at the rate of 6 mm. a year. Using simple arithmetic, one can get a fairly good prediction of future growth. This of course, is an average, and the patient may be an average. To cut down the risk of this, the doctor usually measures leg length using special X-ray technique (called a Scanogram) on three occasions over at least one year duration to estimate growth per year. He may also do an X-ray of the left hand to estimate the bone age (which in some cases may differ from chronological age) by comparing it with an atlas of bone age. In most cases, however, the bone age and chronological age are quite close. Another method of predicting final LLD is by using Anderson and Green?s remaining growth charts. This is a very cumbersome method, but was till the 1970?s, the only method of predicting remaining growth. More recently, however, a much more convenient method of predicting LLD was discovered by Dr. Colin Moseley from Montreal. His technique of using straight line graphs to plot growth of leg lengths is now the most widely used method of predicting leg length discrepancy. Whatever method your doctor uses, over a period of one or two years, once he has a good idea of the final LLD, he can then formulate a plan to equalize leg lengths. Epiphyseodesis is usually done in the last 2 to 3 years of growth, giving a maximum correction of about 5 cm. Leg lengthening can be done at any age, and can give corrections of 5 to10 cm., or more.
The bone is lengthened by surgically applying an external fixation device to the leg. The external fixator, a scaffold-like frame, is connected to the bone with wires, pins, or both. A small crack is made in the bone and the frame creates tension when the patient or family member turns its dial. This is done several times each day. The lengthening process begins approximately five to 10 days after surgery. The bone may lengthen 1 millimeter per day, or approximately 1 inch per month. Lengthening may be slower in a bone that was previously injured. It may also be slower if the leg was operated on before. Bones in patients with potential blood vessel abnormalities, such as cigarette smokers, may also need to be lengthened more slowly. The external fixator is worn until the bone is strong enough to support the patient safely. This usually takes about three months for each inch. Factors such as age, health, smoking and participation in rehabilitation can affect the amount of time needed.

Causes
Sometimes the cause of LLD is unknown, yet the pattern or combination of conditions is consistent with a certain abnormality. Examples include underdevelopment of the inner or outer side of the leg (hemimelias) or (partial) inhibition of growth of one side of the body of unknown cause (hemihypertrophy). These conditions are present at birth, but the limb length difference may be too small to be detected. As the child grows, the LLD increases and becomes more noticeable. In hemimelia, one of the two bones between the knee and the ankle (tibia or fibula) is abnormally short. There also may be associated foot or knee abnormalities. Hemihypertrophy or hemiatrophy are rare conditions in which there is a difference in length of both the arm and leg on only one side of the body. There may also be a difference between the two sides of the face. Sometimes no cause can be found. This type of limb length is called idiopathic. While there is a cause, it cannot be determined using currect diagnostic methods.
Symptoms
The effects of limb length discrepancy vary from patient to patient, depending on the cause and size of the difference. Differences of 3 1/2 percent to 4 percent of the total length of the leg (about 4 cm or 1 2/3 inches in an average adult) may cause noticeable abnormalities when walking. These differences may require the patient to exert more effort to walk. There is controversy about the effect of limb length discrepancy on back pain. Some studies show that people with a limb length discrepancy have a greater incidence of low back pain and an increased susceptibility to injuries. Other studies do not support this finding.
Diagnosis
The only way to decipher between anatomical and functional leg length inequalities (you can have both) is by a physical measurement and series of biomechanical tests. It is actually a simple process and gets to the true cause of some runner?s chronic foot, knee, hip and back pain. After the muscles are tested and the legs are measured it may be necessary to get a special X-ray that measures both of your thighs (Femurs) and legs (Tibias). The X-ray is read by a medical radiologist who provides a report of the actual difference down to the micrometer leaving zero room for error. Once the difference in leg length is known, the solution becomes clear.
Non Surgical Treatment
The key to treatment of LLD in a child is to predict what the discrepancy is at maturity. If it is predicted to be less than 2 cm., no treatment is needed. Limb length discrepancies of up to 2 or 2.5 cm. can be compensated very well with a lift in the shoe. Beyond 2.5 cm., it becomes increasingly difficult to compensate with a left in the insole. Building up the shoe becomes uncosmetic and cumbersome, and some other way of compensating for the discrepancy becomes necessary. The treatment of LLD is long-term treatment, and involves the physician and patient?s family working together as a team. The family needs to weigh the various options available. If leg lengthening is decided on, the family needs to understand the commitment necessary to see it through. The treatment takes 6 months to a year for completion, and complications can happen. But when it works, the results are gratifying.

bestshoelifts
Surgical Treatment
Surgical treatments vary in complexity. Sometimes the goal of surgery is to stop the growth of the longer limb. Other times, surgeons work to lengthen the shorter limb. Orthopedic surgeons may treat children who have limb-length conditions with one or a combination of these surgical techniques. Bone resection. An operation to remove a section of bone, evening out the limbs in teens or adults who are no longer growing. Epiphyseal stapling. An operation to slow the rate of growth of the longer limb by inserting staples into the growth plate, then removing them when the desired result is achieved. Epiphysiodesis. An operation to slow the rate of growth of the longer limb by creating a permanent bony ridge near the growth plate. Limb lengthening. A procedure (also called distraction osteogenesis or the Ilizarov procedure) that involves attaching an internal or external fixator to a limb and gradually pulling apart bone segments to grow new bone between them. There are several ways your doctor can predict the final LLD, and thus the timing of the surgery. The easiest way is the so-called Australian method, popularised by Dr. Malcolm Menelaus, an Australian orthopedic surgeon. According to this method, growth in girls is estimated to stop at age 14, and in boys at age 16 years. The femur grows at the rate of 10 mm. a year, and the upper tibia at the rate of 6 mm. a year. Using simple arithmetic, one can get a fairly good prediction of future growth. This of course, is an average, and the patient may be an average. To cut down the risk of this, the doctor usually measures leg length using special X-ray technique (called a Scanogram) on three occasions over at least one year duration to estimate growth per year. He may also do an X-ray of the left hand to estimate the bone age (which in some cases may differ from chronological age) by comparing it with an atlas of bone age. In most cases, however, the bone age and chronological age are quite close. Another method of predicting final LLD is by using Anderson and Green?s remaining growth charts. This is a very cumbersome method, but was till the 1970?s, the only method of predicting remaining growth. More recently, however, a much more convenient method of predicting LLD was discovered by Dr. Colin Moseley from Montreal. His technique of using straight line graphs to plot growth of leg lengths is now the most widely used method of predicting leg length discrepancy. Whatever method your doctor uses, over a period of one or two years, once he has a good idea of the final LLD, he can then formulate a plan to equalize leg lengths. Epiphyseodesis is usually done in the last 2 to 3 years of growth, giving a maximum correction of about 5 cm. Leg lengthening can be done at any age, and can give corrections of 5 to10 cm., or more.
Functional Leg Length Discrepancy Causes
Overview
Surgery is another option. In some cases the longer extremity can be shortened, but a major shortening may weaken the muscles of the extremity. In growing children, lower extremities can also be equalized by a surgical procedure that stops the growth at one or two sites of the longer extremity, while leaving the remaining growth undisturbed. Your physician can tell you how much equalization can be attained by surgically halting one or more growth centers. The procedure is performed under X-ray control through very small incisions in the knee area. This procedure will not cause an immediate correction in length. Instead, the LLD will gradually decrease as the opposite extremity continues to grow and "catch up." Timing of the procedure is critical; the goal is to attain equal length of the extremities at skeletal maturity, usually in the mid- to late teens. Disadvantages of this option include the possibility of slight over-correction or under-correction of the LLD and the patient?s adult height will be less than if the shorter extremity had been lengthened. Correction of significant LLDs by this method may make a patient?s body look slightly disproportionate because of the shorter legs.
Causes
Common causes include bone infection, bone diseases, previous injuries, or broken bones. Other causes may include birth defects, arthritis where there is a loss of articular surface, or neurological conditions.
Symptoms
The patient/athlete may present with an altered gait (such as limping) and/or scoliosis and/or low back pain. Lower extremity disorders are possibly associated with LLD, some of these are increased hip pain and degeneration (especially involving the long leg). Increased risk of: knee injury, ITB syndrome, pronation and plantar fascitis, asymmetrical strength in lower extremity. Increased disc or vertebral degeneration. Symptoms vary between patients, some patients may complain of just headaches.
Diagnosis
A systematic and well organized approach should be used in the diagnosis of LLD to ensure all relevant factors are considered and no clues are overlooked which could explain the difference. To determine the asymmetry a patient should be evaluated whilst standing and walking. During the process special care should be used to note the extent of pelvic shift from side to side and deviation along the plane of the front or leading leg as well as the traverse deviation of the back leg and abnormal curvature of the spine. Dynamic gait analysis should be conducted during waling where observation of movement on the sagittal, frontal and transverse planes should be noted. Also observe head, neck and shoulder movements for any tilting.
Non Surgical Treatment
A properly made foot orthotic can go a long way in substituting additional millimeters or centimeter on the deficient side. Additional full length inserts are added to the shorter side bringing the runner closer to symmetrical. Heel lifts do not work in runners because when you run you may land on your heel but the rest of the time you are on your forefoot then your toes pushing off. The right custom-made, biomechanical orthotic can address the underlying cause of your pain. Abnormal joint position, overpronation or foot rigidity can be addressed and the biomechanics normalized. San Diego Running Institute orthotics are custom molded to your foot and are designed with your specific body weight, leg length discrepancy, and activity in mind. The restoration of correct mechanical function takes the abnormal stress from the uneven side and allows the body to heal naturally.

functional leg length discrepancy treatment
Surgical Treatment
Lengthening is usually done by corticotomy and gradual distraction. This technique can result in lengthenings of 25% or more, but typically lengthening of 15%, or about 6 cm, is recommended. The limits of lengthening depend on patient tolerance, bony consolidation, maintenance of range of motion, and stability of the joints above and below the lengthened limb. Numerous fixation devices are available, such as the ring fixator with fine wires, monolateral fixator with half pins, or a hybrid frame. The choice of fixation device depends on the desired goal. A monolateral device is easier to apply and better tolerated by the patient. The disadvantages of monolateral fixation devices include the limitation of the degree of angular correction that can concurrently be obtained; the cantilever effect on the pins, which may result in angular deformity, especially when lengthening the femur in large patients; and the difficulty in making adjustments without placing new pins. Monolateral fixators appear to have a similar success rate as circular fixators, especially with more modest lengthenings (20%).
Surgery is another option. In some cases the longer extremity can be shortened, but a major shortening may weaken the muscles of the extremity. In growing children, lower extremities can also be equalized by a surgical procedure that stops the growth at one or two sites of the longer extremity, while leaving the remaining growth undisturbed. Your physician can tell you how much equalization can be attained by surgically halting one or more growth centers. The procedure is performed under X-ray control through very small incisions in the knee area. This procedure will not cause an immediate correction in length. Instead, the LLD will gradually decrease as the opposite extremity continues to grow and "catch up." Timing of the procedure is critical; the goal is to attain equal length of the extremities at skeletal maturity, usually in the mid- to late teens. Disadvantages of this option include the possibility of slight over-correction or under-correction of the LLD and the patient?s adult height will be less than if the shorter extremity had been lengthened. Correction of significant LLDs by this method may make a patient?s body look slightly disproportionate because of the shorter legs.

Causes
Common causes include bone infection, bone diseases, previous injuries, or broken bones. Other causes may include birth defects, arthritis where there is a loss of articular surface, or neurological conditions.
Symptoms
The patient/athlete may present with an altered gait (such as limping) and/or scoliosis and/or low back pain. Lower extremity disorders are possibly associated with LLD, some of these are increased hip pain and degeneration (especially involving the long leg). Increased risk of: knee injury, ITB syndrome, pronation and plantar fascitis, asymmetrical strength in lower extremity. Increased disc or vertebral degeneration. Symptoms vary between patients, some patients may complain of just headaches.
Diagnosis
A systematic and well organized approach should be used in the diagnosis of LLD to ensure all relevant factors are considered and no clues are overlooked which could explain the difference. To determine the asymmetry a patient should be evaluated whilst standing and walking. During the process special care should be used to note the extent of pelvic shift from side to side and deviation along the plane of the front or leading leg as well as the traverse deviation of the back leg and abnormal curvature of the spine. Dynamic gait analysis should be conducted during waling where observation of movement on the sagittal, frontal and transverse planes should be noted. Also observe head, neck and shoulder movements for any tilting.
Non Surgical Treatment
A properly made foot orthotic can go a long way in substituting additional millimeters or centimeter on the deficient side. Additional full length inserts are added to the shorter side bringing the runner closer to symmetrical. Heel lifts do not work in runners because when you run you may land on your heel but the rest of the time you are on your forefoot then your toes pushing off. The right custom-made, biomechanical orthotic can address the underlying cause of your pain. Abnormal joint position, overpronation or foot rigidity can be addressed and the biomechanics normalized. San Diego Running Institute orthotics are custom molded to your foot and are designed with your specific body weight, leg length discrepancy, and activity in mind. The restoration of correct mechanical function takes the abnormal stress from the uneven side and allows the body to heal naturally.

functional leg length discrepancy treatment
Surgical Treatment
Lengthening is usually done by corticotomy and gradual distraction. This technique can result in lengthenings of 25% or more, but typically lengthening of 15%, or about 6 cm, is recommended. The limits of lengthening depend on patient tolerance, bony consolidation, maintenance of range of motion, and stability of the joints above and below the lengthened limb. Numerous fixation devices are available, such as the ring fixator with fine wires, monolateral fixator with half pins, or a hybrid frame. The choice of fixation device depends on the desired goal. A monolateral device is easier to apply and better tolerated by the patient. The disadvantages of monolateral fixation devices include the limitation of the degree of angular correction that can concurrently be obtained; the cantilever effect on the pins, which may result in angular deformity, especially when lengthening the femur in large patients; and the difficulty in making adjustments without placing new pins. Monolateral fixators appear to have a similar success rate as circular fixators, especially with more modest lengthenings (20%).
What Is Mortons Neuroma
Overview
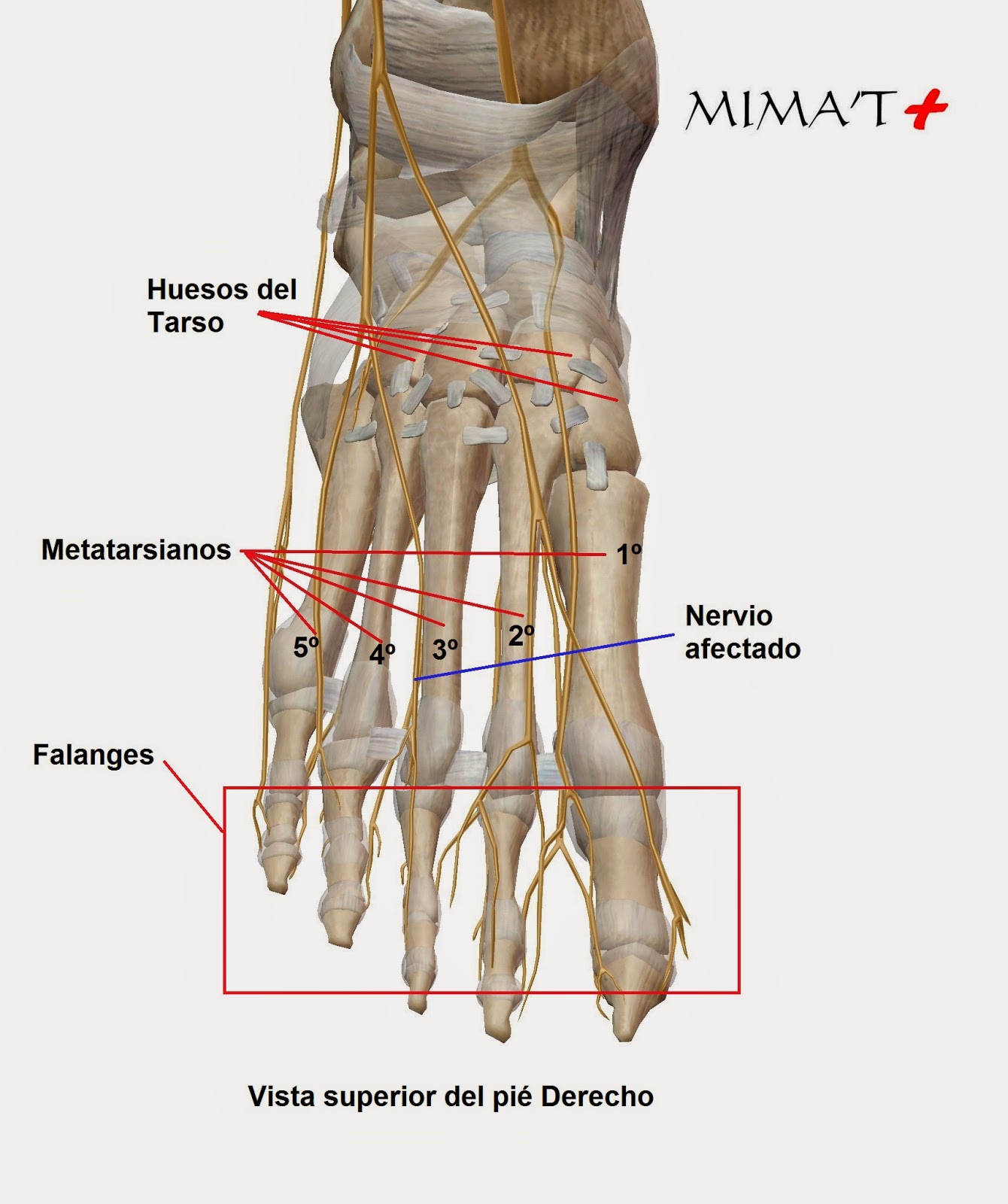 Morton's neuroma is an enlarged nerve that usually occurs in the third interspace, which is between the third and fourth toes. To understand Morton's neuroma further, it may be helpful to look at the anatomy of the foot. Problems often develop in the third interspace because part of the lateral plantar nerve combines with part of the medial plantar nerve here. When the two nerves combine, they are typically larger in diameter than those going to the other toes. Also, the nerve lies in subcutaneous tissue, just above the fat pad of the foot, close to an artery and vein. Above the nerve is a structure called the deep transverse metatarsal ligament. This ligament is very strong, holds the metatarsal bones together, and creates the ceiling of the nerve compartment. With each step, the ground pushes up on the enlarged nerve and the deep transverse metatarsal ligament pushes down. This causes compression in a confined space.
Morton's neuroma is an enlarged nerve that usually occurs in the third interspace, which is between the third and fourth toes. To understand Morton's neuroma further, it may be helpful to look at the anatomy of the foot. Problems often develop in the third interspace because part of the lateral plantar nerve combines with part of the medial plantar nerve here. When the two nerves combine, they are typically larger in diameter than those going to the other toes. Also, the nerve lies in subcutaneous tissue, just above the fat pad of the foot, close to an artery and vein. Above the nerve is a structure called the deep transverse metatarsal ligament. This ligament is very strong, holds the metatarsal bones together, and creates the ceiling of the nerve compartment. With each step, the ground pushes up on the enlarged nerve and the deep transverse metatarsal ligament pushes down. This causes compression in a confined space.
Causes
A Morton's Neuroma is not a true neuroma, which is a tumor that is generally benign. Rather, it is an enlargement of the nerve where it goes between the metatarsal bones of the foot. Because the nerve no longer fits between the gap, the pressure causes pain and sometimes numbness. This enlargement of the nerve is often an inflammation due to irritation. If the forefoot becomes compressed due to shoes that are too narrow, the nerve becomes damaged and inflamed. This inflammation means the nerve no longer fits in the space between the bones, creating further irritation and more inflammation. If this vicious circle can be broken, the problem may be resolved. However, in some situations the nerve can have fibrous tissues formed around it, which may require the destruction of the nerve or surgical removal.
Symptoms
Patients will complain of numbness, a ?pins and needles? type of tingling and loss of sensation in the toes. Burning pain in the ball of the foot that may radiate into the toes. The pain generally intensifies with activity or wearing shoes. Night pain is rare. There may also be numbness in the toes, or an unpleasant feeling in the toes. Runners may feel pain as they push off from the starting block. High-heeled shoes, which put the foot in a similar position to the push-off, can also aggravate the condition. Tight, narrow shoes also aggravate this condition by compressing the toe bones and pinching the nerve.
Diagnosis
To confirm the diagnosis, your doctor will examine your feet. He or she will look for areas of tenderness, swelling, calluses, numbness, muscle weakness and limited motion. To check for a Morton's neuroma, your doctor will squeeze the sides of your foot. Squeezing should compress the neuroma and trigger your typical pain. In some cases, your doctor will find numbness in the webbed area between the affected toes. Pain in two or more locations on one foot, such as between both the second and third toes and the third and fourth toes, more likely indicates that the toe joints are inflamed rather than a Morton' neuroma.
Non Surgical Treatment
If you have Morton's neuroma, shoes with a wider toe area may be recommended. You can also take painkillers to help ease the pain. Steroid injections may also be given to treat the affected nerve. If these treatments don't work, surgery may be needed. This involves removing the thickened tissue around the nerve (and sometimes the nerve itself) to release the pressure.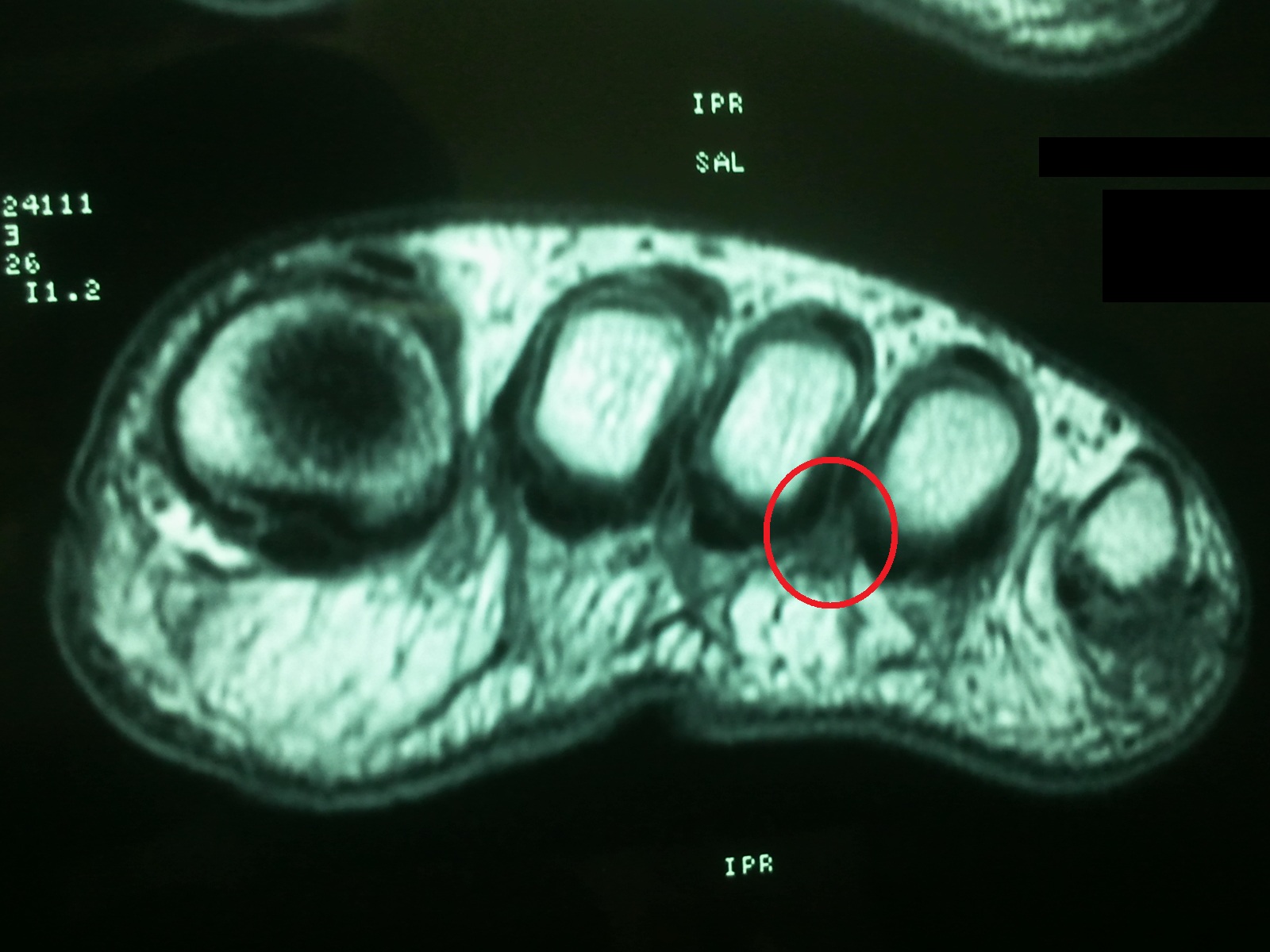
Surgical Treatment
Surgery for Morton's neuroma is usually a treatment of last resort. It may be recommended if you have severe pain in your foot or if non-surgical treatments haven't worked. Surgery is usually carried out under local anaesthetic, on an outpatient basis, which means you won't need to stay in hospital overnight. The operation can take up to 30 minutes. The surgeon will make a small incision, either on the top of your foot or on the sole. They may try to increase the space around the nerve (nerve decompression) by removing some of the surrounding tissue, or they may remove the nerve completely (nerve resection). If the nerve is removed, the area between your toes may be permanently numb. After the procedure you'll need to wear a special protective shoe until the affected area has healed sufficiently to wear normal footwear. It can take up to four weeks to make a full recovery. Most people (about 75%) who have surgery to treat Morton's neuroma have positive results and their painful symptoms are relieved.
 Morton's neuroma is an enlarged nerve that usually occurs in the third interspace, which is between the third and fourth toes. To understand Morton's neuroma further, it may be helpful to look at the anatomy of the foot. Problems often develop in the third interspace because part of the lateral plantar nerve combines with part of the medial plantar nerve here. When the two nerves combine, they are typically larger in diameter than those going to the other toes. Also, the nerve lies in subcutaneous tissue, just above the fat pad of the foot, close to an artery and vein. Above the nerve is a structure called the deep transverse metatarsal ligament. This ligament is very strong, holds the metatarsal bones together, and creates the ceiling of the nerve compartment. With each step, the ground pushes up on the enlarged nerve and the deep transverse metatarsal ligament pushes down. This causes compression in a confined space.
Morton's neuroma is an enlarged nerve that usually occurs in the third interspace, which is between the third and fourth toes. To understand Morton's neuroma further, it may be helpful to look at the anatomy of the foot. Problems often develop in the third interspace because part of the lateral plantar nerve combines with part of the medial plantar nerve here. When the two nerves combine, they are typically larger in diameter than those going to the other toes. Also, the nerve lies in subcutaneous tissue, just above the fat pad of the foot, close to an artery and vein. Above the nerve is a structure called the deep transverse metatarsal ligament. This ligament is very strong, holds the metatarsal bones together, and creates the ceiling of the nerve compartment. With each step, the ground pushes up on the enlarged nerve and the deep transverse metatarsal ligament pushes down. This causes compression in a confined space.Causes
A Morton's Neuroma is not a true neuroma, which is a tumor that is generally benign. Rather, it is an enlargement of the nerve where it goes between the metatarsal bones of the foot. Because the nerve no longer fits between the gap, the pressure causes pain and sometimes numbness. This enlargement of the nerve is often an inflammation due to irritation. If the forefoot becomes compressed due to shoes that are too narrow, the nerve becomes damaged and inflamed. This inflammation means the nerve no longer fits in the space between the bones, creating further irritation and more inflammation. If this vicious circle can be broken, the problem may be resolved. However, in some situations the nerve can have fibrous tissues formed around it, which may require the destruction of the nerve or surgical removal.
Symptoms
Patients will complain of numbness, a ?pins and needles? type of tingling and loss of sensation in the toes. Burning pain in the ball of the foot that may radiate into the toes. The pain generally intensifies with activity or wearing shoes. Night pain is rare. There may also be numbness in the toes, or an unpleasant feeling in the toes. Runners may feel pain as they push off from the starting block. High-heeled shoes, which put the foot in a similar position to the push-off, can also aggravate the condition. Tight, narrow shoes also aggravate this condition by compressing the toe bones and pinching the nerve.
Diagnosis
To confirm the diagnosis, your doctor will examine your feet. He or she will look for areas of tenderness, swelling, calluses, numbness, muscle weakness and limited motion. To check for a Morton's neuroma, your doctor will squeeze the sides of your foot. Squeezing should compress the neuroma and trigger your typical pain. In some cases, your doctor will find numbness in the webbed area between the affected toes. Pain in two or more locations on one foot, such as between both the second and third toes and the third and fourth toes, more likely indicates that the toe joints are inflamed rather than a Morton' neuroma.
Non Surgical Treatment
If you have Morton's neuroma, shoes with a wider toe area may be recommended. You can also take painkillers to help ease the pain. Steroid injections may also be given to treat the affected nerve. If these treatments don't work, surgery may be needed. This involves removing the thickened tissue around the nerve (and sometimes the nerve itself) to release the pressure.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery for Morton's neuroma is usually a treatment of last resort. It may be recommended if you have severe pain in your foot or if non-surgical treatments haven't worked. Surgery is usually carried out under local anaesthetic, on an outpatient basis, which means you won't need to stay in hospital overnight. The operation can take up to 30 minutes. The surgeon will make a small incision, either on the top of your foot or on the sole. They may try to increase the space around the nerve (nerve decompression) by removing some of the surrounding tissue, or they may remove the nerve completely (nerve resection). If the nerve is removed, the area between your toes may be permanently numb. After the procedure you'll need to wear a special protective shoe until the affected area has healed sufficiently to wear normal footwear. It can take up to four weeks to make a full recovery. Most people (about 75%) who have surgery to treat Morton's neuroma have positive results and their painful symptoms are relieved.
Shoe Lifts The Industry experts Option For Leg Length Discrepancy
There are actually two different types of leg length discrepancies, congenital and acquired. Congenital implies that you are born with it. One leg is anatomically shorter than the other. As a result of developmental periods of aging, the brain picks up on the gait pattern and recognizes some variance. The human body usually adapts by tilting one shoulder over to the "short" side. A difference of under a quarter inch isn't blatantly irregular, require Shoe Lifts to compensate and usually does not have a profound effect over a lifetime.

Leg length inequality goes largely undiscovered on a daily basis, yet this condition is easily corrected, and can eradicate many cases of back discomfort.
Therapy for leg length inequality typically consists of Shoe Lifts. They are economical, commonly costing under twenty dollars, in comparison to a custom orthotic of $200 plus. When the amount of leg length inequality begins to exceed half an inch, a whole sole lift is generally the better choice than a heel lift. This prevents the foot from being unnecessarily stressed in an abnormal position.
Back ache is the most common health problem impacting men and women today. Over 80 million people are affected by back pain at some point in their life. It's a problem that costs businesses huge amounts of money annually because of lost time and production. Fresh and more effective treatment solutions are constantly sought after in the hope of reducing the economical impact this condition causes.

Men and women from all corners of the world suffer from foot ache due to leg length discrepancy. In these types of cases Shoe Lifts might be of very beneficial. The lifts are capable of eliminating any pain and discomfort in the feet. Shoe Lifts are recommended by many certified orthopaedic doctors.
So as to support the human body in a well-balanced manner, feet have a vital function to play. In spite of that, it is sometimes the most neglected zone of the human body. Some people have flat-feet which means there is unequal force placed on the feet. This will cause other parts of the body like knees, ankles and backs to be affected too. Shoe Lifts make sure that suitable posture and balance are restored.

Leg length inequality goes largely undiscovered on a daily basis, yet this condition is easily corrected, and can eradicate many cases of back discomfort.
Therapy for leg length inequality typically consists of Shoe Lifts. They are economical, commonly costing under twenty dollars, in comparison to a custom orthotic of $200 plus. When the amount of leg length inequality begins to exceed half an inch, a whole sole lift is generally the better choice than a heel lift. This prevents the foot from being unnecessarily stressed in an abnormal position.
Back ache is the most common health problem impacting men and women today. Over 80 million people are affected by back pain at some point in their life. It's a problem that costs businesses huge amounts of money annually because of lost time and production. Fresh and more effective treatment solutions are constantly sought after in the hope of reducing the economical impact this condition causes.

Men and women from all corners of the world suffer from foot ache due to leg length discrepancy. In these types of cases Shoe Lifts might be of very beneficial. The lifts are capable of eliminating any pain and discomfort in the feet. Shoe Lifts are recommended by many certified orthopaedic doctors.
So as to support the human body in a well-balanced manner, feet have a vital function to play. In spite of that, it is sometimes the most neglected zone of the human body. Some people have flat-feet which means there is unequal force placed on the feet. This will cause other parts of the body like knees, ankles and backs to be affected too. Shoe Lifts make sure that suitable posture and balance are restored.
Just What Is Calcaneal Spur

Overview
There are approximately 75 different causes of heel pain. At least 80% of all heel pain is due to heel spurs. A heel spur contains calcium, but cannot truly be called a calcium deposit. Bone spurs, whether they are on the heel or on any other bone of the body, are true bone -- they are true enlargements of the bone and may be sharp and pointed, or round and knobby. Since bone spurs are true bone, they contain calcium just like regular bones, but are not pure calcium deposits.
Causes
Heel Spur typically occurs in people who have a history of foot pain, and is most often seen in middle-aged men and women. The bony growth itself is not what causes the pain associated with heel spur. The pain is typically caused by inflammation and irritation of the surrounding tissues. Approximately 50% of patients with a heel spur also experience Plantar Fasciitis.

Symptoms
Heel spur and plantar fasciitis pain usually begins in the bottom of the heel, and frequently radiates into the arch. At times, however, the pain may be felt only in the arch. The pain is most intense when first standing, after any period of rest. Most people with this problem experience their greatest pain in the morning, with the first few steps after sleeping. After several minutes of walking, the pain usually becomes less intense and may disappear completely, only to return later with prolonged walking or standing. If a nerve is irritated due to the swollen plantar fascia, this pain may radiate into the ankle. In the early stages of Heel Spurs and Plantar Fasciitis, the pain will usually subside quickly with getting off of the foot and resting. As the disease progresses, it may take longer periods of time for the pain to subside.
Diagnosis
A thorough history and physical exam is always necessary for the proper diagnosis of heel spurs and other foot conditions. X rays of the heel area are helpful, as excess bone production will be visible.
Non Surgical Treatment
Conventional treatment for heel spurs typically includes rest, stretching exercises, icing and anti-inflammatory medications. Many people find it difficult to go through the day without some sort of routine activity or exercise, and this prolongs the heel spur and forces people to rely on anti-inflammatory medications for a longer period of time. This can be detrimental due to the many side effects of these medications, including gastrointestinal problems like leaky gut, bleeding and ulcer symptoms.
Surgical Treatment
Approximately 2% of people with painful heel spurs need surgery, meaning that 98 out of 100 people do well with the non-surgical treatments previously described. However, these treatments can sometimes be rather long and drawn out, and may become considerably expensive. Surgery should be considered when conservative treatment is unable to control and prevent the pain. If the pain goes away for a while, and continues to come back off and on, despite conservative treatments, surgery should be considered. If the pain really never goes away, but reaches a plateau, beyond which it does not improve despite conservative treatments, surgery should be considered. If the pain requires three or more injections of "cortisone" into the heel within a twelve month period, surgery should be considered.
Prevention
You can help prevent heel spur symptoms from returning by wearing the proper shoes. Customized orthotics and insoles can help relieve pressure. It is important to perform your exercises to help keep your foot stretched and relaxed.